Store and Retrieve Data Using Literal and Variable Values in C#
C# is a strongly typed language, meaning that every variable must be declared with a specific type, and values assigned to it must be compatible with that type.
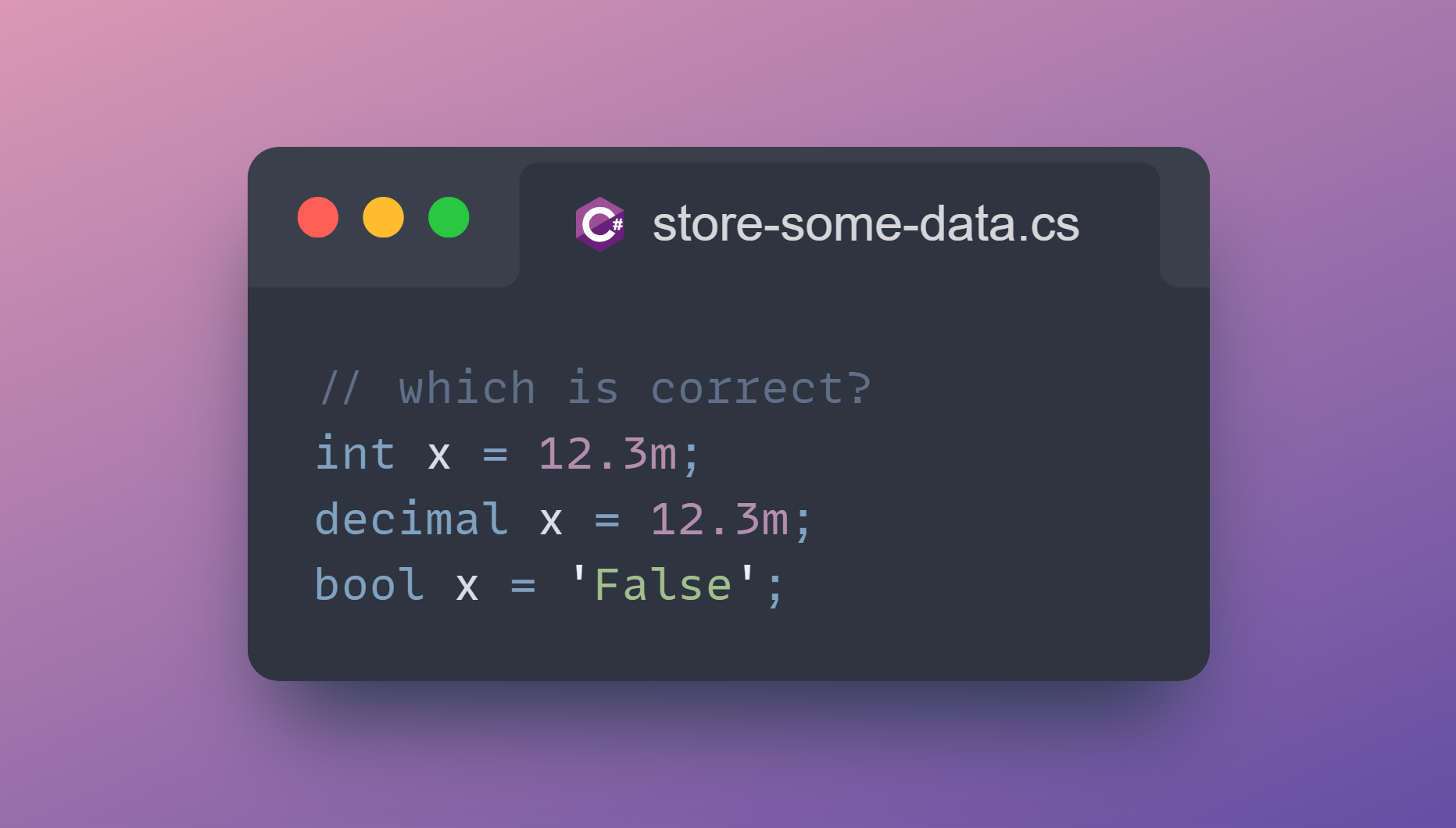
Question
Which of the following lines of code creates a variable correctly?
Try to answer this question first on freeCodeCamp .
Option 1
int x = 12.3m;Here, we’re declaring a variable x of type
int
. The key point to remember is that int is used for whole numbers not decimals.
We’re then trying to assign it to the value 12.3m. The presence of a decimal point makes this a
floating-point
value, and the m suffix is the literal for a decimal.
C# is a strongly typed language
and enforces type safety. Assigning a decimal value to an int variable is not allowed as it would lead to data loss. This kind of mismatch causes a compiler error.
This is incorrect.
Option 2
decimal x = 12.3m;Here, we’re declaring a variable x of type
decimal
and assign the literal 12.3m. The m suffix is the literal for a decimal. This tells the compiler this is a decimal, not a double (which would be the default for floating-point literals without a suffix).
This is the correct answer.
Option 3
bool x = 'False';Here, we’re declaring a variable x of type
bool
.
A bool can can either be true or false.
Next we assign x to the value 'False' enclosed in single quotes which in C# denotes a
char
(a single character).
Since 'False' is actually multiple characters, this won’t compile either.
If you wanted to assign a bool with the value false, you would write:
bool x = false;This is incorrect.
